Product and Platform
Highlights
- Analysts, data migration consultants, extract, transform, and load (ETL) developers, and others in IT roles face challenges migrating multi-tenant data involving heterogeneous source-target database (DB) systems within a stipulated time.
- The multi-tenant data migration factory solution tackles challenges from the intricacies, time, manual efforts, heterogeneous source-target mappings, and other data domain features to ensure operational stability.
- This factory-based approach goes beyond expediting the data pipeline to optimize component reuse and achieve multiple migrations simultaneously.
On this page
Solution reuse
Continuous technological advancement necessitates organizations to transform their business applications and IT systems to align with new technologies and optimize their investments. This transformation may be from legacy to modern systems, from on-premises to cloud (Platform-as-a-service), or in-house to cloud-hosted (Software-as-a-service) solutions. It involves migrating large-scale data from multiple customer data stores to a customized platform in the target system.
Example: Customer A and customer B have their source data residing on two different platforms/DBs, but both systems are migrating data into a single platform/DB.
While organizations are testing agility, automation, and time-saving strategies related to migration activities, the increasing demand for minimizing efforts through solution reusability remains constant. Thus, a solution has emerged to leverage the data migration factory setup as a multi-tenant, multi-source, and multi-country factory model to migrate customer data into a single, customized platform in the target system. This enables the execution of multiple large-scale data migration instances from varied sources.
Courrent challenges
Data migration comes with its own set of challenges. Application data, the main component of business transformations, must be migrated seamlessly into the target system to ensure business continuity. This involves data transformation, which can be complex, time-consuming, and error prone as data moves between systems. The system or application teams require more knowledge of the source and the target.
Multiple simultaneous data migration instances require a solution to optimize the effort involved as we onboard source data from various customers on the target system, incurring considerable infrastructure costs. During factory-based data migration, the source and target data model structures are often complex. Security and compliance requirements necessitate the separation of end customer data. Using masked data in development or test environments is essential when performing migration activities with offshore resources.
Enhanced enablers
To address these complexities, this paper brings into perspective effective ways of defining and setting up the data migration factory, such as:
- Reusing processes, metadata, mappings, and configuration
- Adopting automation
- Using tools to improve productivity
- Complying with data privacy regulations
- Providing technical and operational metrics to meet security requirements and compliance obligations
The core of this approach is to use the features of a smart product to migrate data from single or multiple sources to a single, customized target platform. The solution to all data migration challenges is to create an integrated pipeline using different product capabilities such as data quality check (mainly profiling and cleansing), data masking in a factory model, and data transformation. You can reuse this data pipeline multiple times to enhance simultaneous data migration efforts.
Data migration factory enables the reuse of metadata or configuration through intelligent capabilities such as intelligent metadata refresh, fuzzy logic-based auto-mapping, intelligent mapping edit, and import/export capabilities. Such a product’s multi-tenancy capability also allows data segregation across all users to ensure data privacy and sensitivity.
Unique enablers
Such innovative products leverage various enablers as part of the factory-based data migration. These enablers include:
- Refresh metadata
- Similar schemas from source data models may exist in the factory model, and this enabler can only capture the delta change between the two schemas.
- Using this enabler, users can easily accommodate metadata model changes in the product from the source or the target point of view.
- Intelligent edit
- This enabler can capture delta change highlights, reuse design mappings for unchanged schema parts, and color-coding schema changes (addition/update/deletion).
- Users receive intelligent input to set up migration scripts for newer migration cases and according to different tenants.
- In sync with the metadata refresh capability, intelligent edit highlights the delta part in the mapping design for the refreshed metadata to incorporate this change in the subsequent migration.
- Clone mapping design
- The mapping design is the source table(s) to target table data migration configuration for a particular scenario.
- These products can copy such a configuration setting and clone it for faster redesign of similar migration scenarios.
- Such products can also maintain versions of a configuration setting, thereby assisting in higher reusability.
- Import/export mapping configuration
- Import and export works for the business application, along with its metadata or mappings.
- It is valid for both source and target.
- This enabler allows users to leverage the existing configurations as a baseline and customize further migrations with minimal effort.
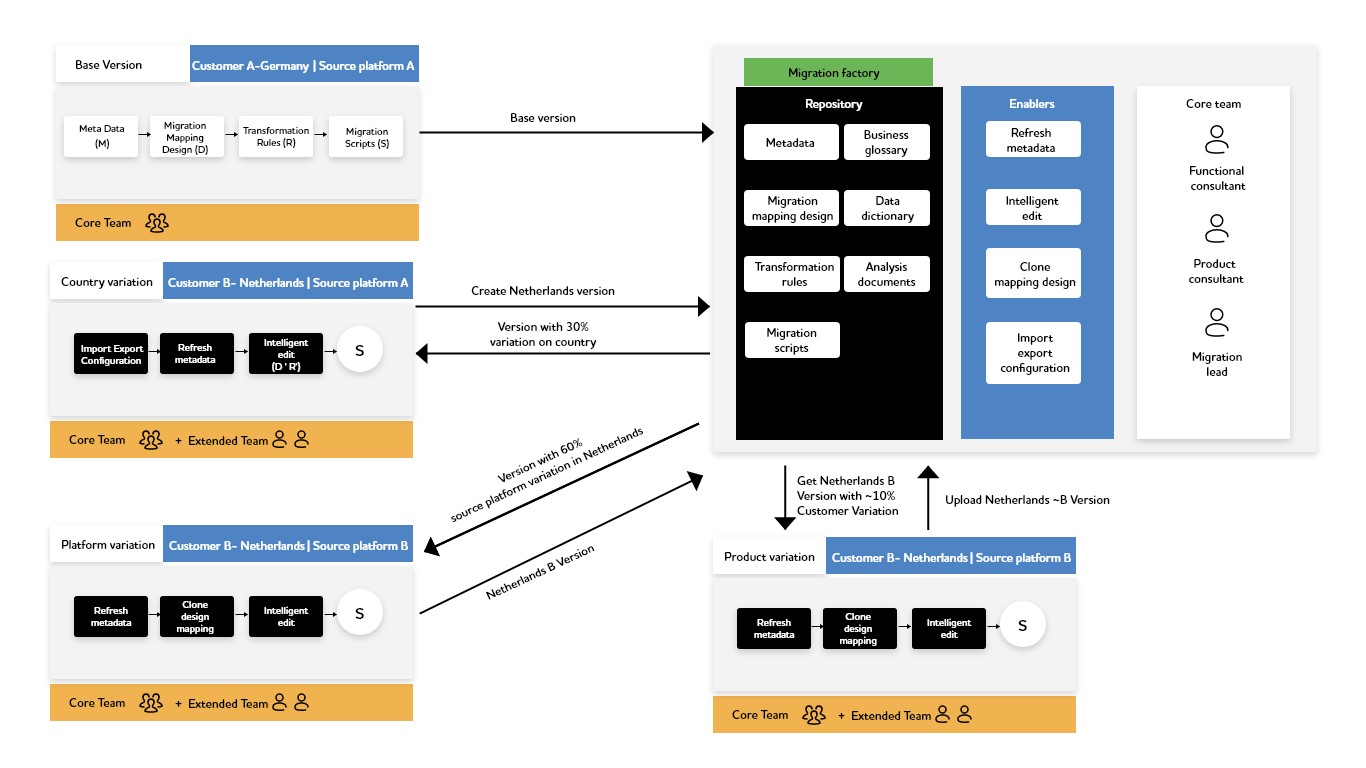
A deeper understanding of the factory-based data migration model is depicted in the following figure.
This image depicts the data migration factory enablement through different product enablers with diverse variations in source systems such as country, platform, or product.
First, the base version is configured based on the standard steps involved in data migration. This acts as the baseline for further migrations.
The solution's reuse depends on the similarity of the metadata models of the different source systems. With minimal intervention with the existing base version, optimal use of similarity, and the intelligent features of such products, the data migration factory performs multiple migrations optimally.
Best practices
As a result, organizations can anticipate gaining the following benefits when they reuse the factory setup:
- It improves onboarding time for new customers by reducing the time taken for each new customer configuration. This is possible by reusing factory components to migrate their data effectively and efficiently, leveraging the product's intelligent capabilities.
- Reduces manual tasks and effort as multiple automation processes expedited data processing efficiently.
- Effective cost savings result from reusing the same data pipeline to perform multiple data migrations.
- Additionally, it is an offshore-based factory model, making it a cost-effective solution.
The factory-based data migration solution offers the following as best practices resulting from the approach:
- The solution provides customers an effective way of setting up the data migration pipeline using different capabilities of such products.
- It allows for effective collaboration and coordination among all the stakeholders involved.
- It enables an effective way of creating and capturing the migration strategy planning and execution details.
Business use case
The data migration factory solution approach offers numerous business benefits, particularly in merger-related scenarios. For instance, in industries such as banking, insurance, and others, where merging multiple organizations into a single entity is planned, efficient, and large-scale data migration to a single target platform is essential. In such cases, the factory-based data migration approach proves to be an effective and constructive solution.